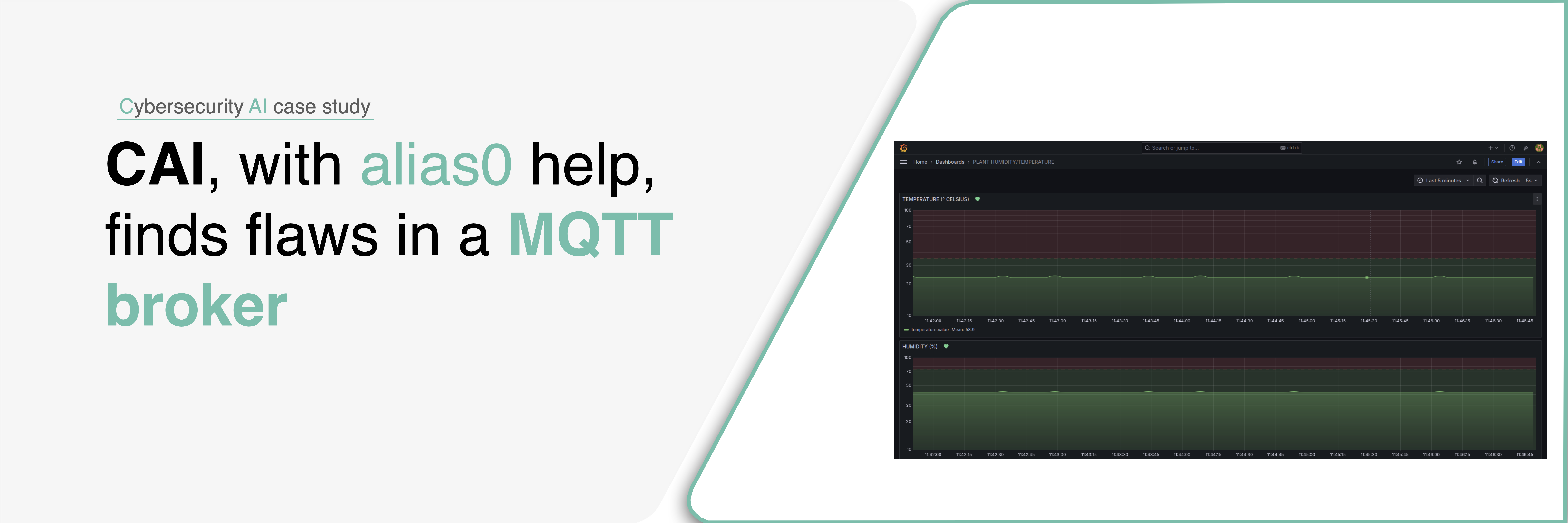

This study analyzes a SCADA system built on Grafana, deployed in a Dockerized environment to monitor temperature and humidity levels within an industrial plant. Testing revealed major security flaws in its MQTT communication architecture, including unauthenticated topic subscriptions, lack of message integrity verification, and absence of encryption.
During the CAI-driven exercise, the system’s OT network was mapped, revealing an IIoT device responsible for publishing environmental telemetry. CAI successfully subscribed to the MQTT topics without authentication and injected falsified temperature and humidity readings—such as 65 °C and 95% RH—directly into the data stream. These manipulated values were displayed through Grafana dashboards, compromising data integrity and operator trust in the system’s supervisory control.

This video demonstrates the operation of CAI (Cybersecurity AI) targeting an unsecured MQTT broker within a Docker-virtualized industrial OT network. CAI connects without authentication and, after passively identifying topics related to temperature and humidity, injects falsified environmental readings—such as 65 °C and 95% RH—into the message stream. These manipulated values are then reflected in real time through a Grafana-based SCADA interface, compromising the integrity of telemetry and misleading operators responsible for supervisory control.
CAI represents the first open-source framework specifically designed to democratize advanced security testing through specialized AI agents. By 2028, most cybersecurity actions will be autonomous, with humans teleoperating, making CAI's approach to AI-powered vulnerability discovery increasingly critical for organizational security. The framework transcends theoretical benchmarks by enabling practical security outcomes. CAI achieved first place among AI teams and secured a top-20 position worldwide in the "AI vs Human" CTF live Challenge, earning a monetary reward and various other prizes and bounties ever since then. This performance demonstrates that AI-powered security testing can compete with and often exceed human capabilities in vulnerability discovery.
Explore CAI's source code ❯An MQTT broker is a lightweight messaging server that enables efficient, real-time communication between industrial devices using the publish/subscribe model. It plays a central role in IIoT environments by handling data exchange between sensors, controllers, and monitoring systems.
Grafana, on the other hand, is a powerful open-source analytics and visualization platform that connects to the MQTT broker to display real-time telemetry—such as temperature, humidity, or pressure—on customizable dashboards. Together, MQTT and Grafana form a scalable, cost-effective foundation for modern SCADA systems.

17
~0.5 €
Evaluate whether a remote agent could connect to the MQTT broker within a Dockerized OT network, identify critical environmental topics, and inject falsified data without authentication—exposing potential weaknesses in MQTT-based SCADA systems and their lack of topic-level security controls.
Using CAI, Alias Robotics simulated a real-world attack against a Grafana-based SCADA system by exploiting the lack of authentication in its MQTT broker. CAI identified the broker within the Dockerized OT network, connected without credentials, located the temperature and humidity topics, and injected falsified sensor values (e.g., 65 °C and 95% RH). These manipulated readings appeared in real time on the Grafana dashboards, demonstrating the impact of the vulnerability on operator trust and system integrity.
